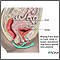
The urinary system consisting of paired kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra is the second commonly infected by infection after the respiratory system.
Maintaining the body’s internal environment within normal limits is the main function of the urinary system.
Urine is formed in the kidneys and passed through a narrow tubes called ureters going to the urinary bladder where it is stored. When the bladder is full urine is excreted through the urethra.
Urine is normally pure and the urinary tract is free from any microorganism not until it is infected by bacteria, viruses and fungi which find their way colonizing the urinary tract and resulted to urinary tract infection (UTI).
Urinary tract infection are classified into two, the lower and the upper. It is lower if only urethra (urethritis) and bladder (cystitis) are involved while the upper involves the ureters (ureteritis) and the kidneys (pyelorephritis). The upper one is more considered the more serious condition than the lower one.
In most UTI cases, women are more prone to infection than men. It can hardly occur to men below fifty years old unless tract stones or any abnormality that prevent the urine to be excreted exists. Men with prostate gland enlargement is susceptible to UTI because it constricts the prompt drainage of urine from the urinary bladder.
Based on statistics, one in every two women would experienced UTI in their lifetime. Many of them has experienced more than once. Probable reasons why women are more vulnerable to UTI are the following:
a) Women’s urethra is much shorter than men four centimeter for women and twenty centimeters for men, thus making it easier for any infection to enter.
b) Women’s urethral orifice is closed to the anus where pathogenic bacteria are predominant. E-coli bacteria that normally reside in the colon or large intestines are most common cause of UTI, it was noted.
c) The urethral orifice which is located just above the vagina is another reason why UTI’s are common to women. The urethra is sometimes irritated during sexual intercourse making it easy target for bacteria.
Microorganisms such as herpes simplex virus and chlamydia that cause sexually transmitted diseases (STD) can easily find their way to urethral orifice.
d) The use of birth control gadgets such as diaphragms or spermicidal agent and the use of irritating feminine products are factors that put women at higher risks for UTI.
Painful urination, frequent and urgent need to urinate, abdominal and backpain, blood in the urine, cloudy and strong or foul smelling urine and fever are among the symptoms of UTI.
Urinary tract infection can be treated by antibiotics or any appropriate antimicrobial agents. UTI’s remotely complicate when treated promptly. If left untreated this can caused chronic kidney infection that can be damaging permanently these organs.
In order to prevent UTI from happening one has to observe the following:
a) Drink plenty of water everyday it can flush out the bacteria from the bladder and the urethra.
b) Don’t hold urine. Empty your bladder often and completely.
c) After bowel movement for women, wipe from front to back fashion so you do not introduce bacteria from the anus to the urethra.
d) Urinate after having sex to help flush away the bacteria.
e) Avoid the use of diaphragms and spermicidal gels.
f) Lastly, minimize the use of deodorant sprays or other products such as douches and powders that can cause irritations to the urethra.